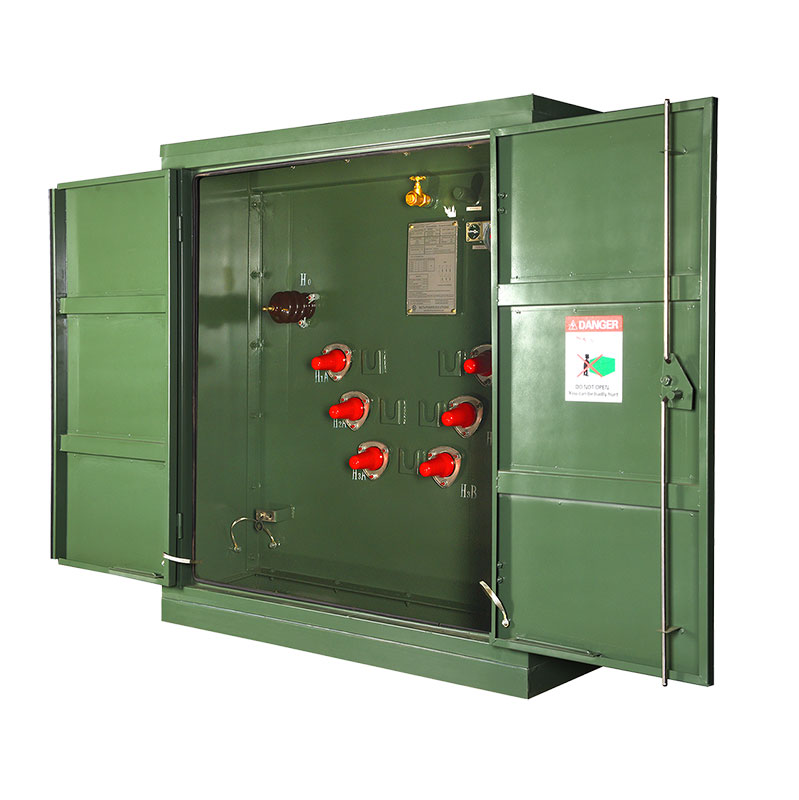
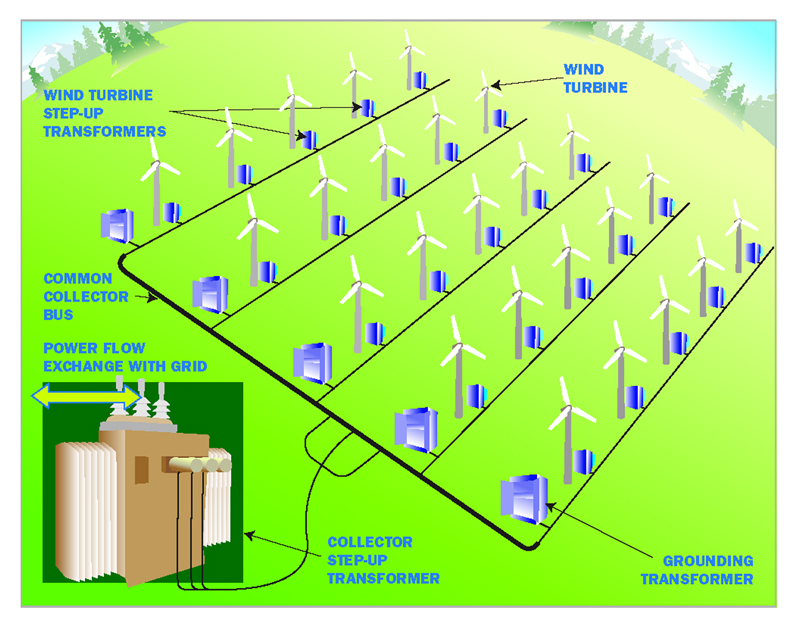
A grounding transformer or earthing transformer is a type of auxiliary transformer used in three-phase electric power systems to provide a ground path to either an ungrounded wye or a delta-connected system. Grounding transformers are part of an earthing system of the network. They let three-phase (delta connected) systems accommodate phase-to-neutral loads by providing a return path for current to a neutral.
Grounding transformers are typically used to:
- Provide a relatively low-impedance path to ground, thereby maintaining the system neutral at or near ground potential.
- Limit the magnitude of transient over voltages when restriking ground faults occur.
- Provide a source of ground fault current during line-to-ground faults.
- Permit the connection of phase-to-neutral loads when desired.
Grounding transformers most commonly incorporate a single winding transformer with a zigzag winding configuration, but may also be created with a (rare case) delta-wye transformer. Neutral grounding transformers are very common on generators in power plants and wind farms. Neutral grounding transformers are sometimes applied on high-voltage (sub-transmission) systems, such as at 33 kV, where the circuit would otherwise not have a ground; for example, if a system is fed by a delta-connected transformer. The grounding point of the transformer may be connected through a resistor or arc suppression coil to limit the fault current on the system in the event of a line-to-ground fault.
References